Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Hydrocarbon compounds and their derivatives >> Hydrocarbon halide |
|---|---|
| Name | 1-Bromo-3-chloropropane |
| Synonyms | 1-Chloro-3-bromopropane; Trimethylene chlorobromide |
| Molecular Structure | 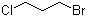 |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6BrCl |
| Molecular Weight | 157.44 |
| CAS Registry Number | 109-70-6 |
| EC Number | 203-697-1 |
| SMILES | C(CCl)CBr |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 1.598 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | -59 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 136.4±13.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 144 - 145 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 38.0±9.9 ºC (Calc.)*, 45 ºC (Expl.) |
| Solubility | water: insoluble (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.468 (Calc.)*, 1.486 (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |



 GHS02;GHS06;GHS07;GHS08 DangerGHS02 Details
GHS02;GHS06;GHS07;GHS08 DangerGHS02 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H226-H302-H315-H319-H331-H332-H335-H341-H412 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P203-P210-P233-P240-P241-P242-P243-P261-P264-P264+P265-P270-P271-P273-P280-P301+P317-P302+P352-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P316-P317-P318-P319-P321-P330-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P370+P378-P403+P233-P403+P235-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 2688 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1‑Bromo‑3‑chloropropane is a halogenated organic compound consisting of a three-carbon alkyl chain substituted with a bromine atom at the first carbon and a chlorine atom at the third carbon. Its molecular formula is C3H6BrCl, and it is a member of the haloalkane class of compounds. The presence of two different halogen atoms on the terminal carbons of the chain imparts unique reactivity, making it a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis and industrial chemistry. Physically, 1‑bromo‑3‑chloropropane is a colorless to pale yellow liquid with moderate solubility in organic solvents and limited solubility in water. The compound is primarily used as a building block in the synthesis of a wide range of organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. Its dual halide functionality allows it to participate in nucleophilic substitution reactions at either end of the molecule, enabling the selective introduction of functional groups. The bromine atom is generally more reactive toward nucleophilic substitution than the chlorine atom due to the weaker C–Br bond and greater polarizability, which provides chemists with the ability to perform sequential transformations in multistep synthesis. Synthesis of 1‑bromo‑3‑chloropropane typically involves halogenation of 1,3‑propanediol or 3‑chloropropanol with hydrobromic acid or other brominating agents. Alternative methods include the reaction of allyl chloride with hydrogen bromide under controlled conditions. Careful control of temperature and stoichiometry is required to minimize side reactions such as polyhalogenation or elimination reactions that can lead to unsaturated by-products. The resulting compound can be purified by distillation, taking advantage of its distinct boiling point relative to unreacted starting materials or side products. Chemically, 1‑bromo‑3‑chloropropane is reactive due to the presence of the two halogens. Both halogen atoms can undergo nucleophilic substitution, with the bromine atom being more susceptible to attack by nucleophiles such as amines, thiols, and alkoxides. The chlorine atom is less reactive, allowing selective functionalization of the bromide first. This selectivity is valuable in the preparation of heterobifunctional molecules, where controlled sequential reactions are necessary. The compound may also undergo elimination reactions under basic conditions to form allylic halides or unsaturated derivatives, though such reactions require careful control to avoid over-elimination. In pharmaceutical chemistry, 1‑bromo‑3‑chloropropane is employed as an intermediate in the preparation of active pharmaceutical ingredients, particularly those containing propyl chains or halogenated substituents. Its ability to serve as a precursor for the introduction of various nucleophilic groups allows the synthesis of amines, ethers, and thioethers. In addition, it can be used in the synthesis of quaternary ammonium salts and other cationic derivatives for use in chemical research or as intermediates for biologically active compounds. In materials chemistry, 1‑bromo‑3‑chloropropane can be used to introduce functional groups onto polymers or surfaces. The molecule’s bifunctional nature enables it to act as a crosslinker or a linker in the formation of complex macromolecules. By reacting selectively with different nucleophiles at each end, researchers can modify polymer chains or small molecules with controlled orientation and functionality. This versatility has made it a useful reagent in synthetic organic chemistry and materials development. From a physical and safety standpoint, 1‑bromo‑3‑chloropropane is moderately volatile and should be handled with appropriate personal protective equipment. It is flammable and can release harmful vapors if improperly stored. The compound is stable under normal conditions but should be kept away from strong bases, oxidizers, and high temperatures to avoid unwanted decomposition or reactions. Overall, 1‑bromo‑3‑chloropropane is a chemically versatile halogenated compound whose dual halide functionality allows selective reactions for the synthesis of a wide range of organic molecules. Its combination of bromine and chlorine atoms, moderate stability, and liquid form make it a valuable reagent in both laboratory and industrial chemistry, particularly for sequential functionalization, bifunctional molecule construction, and intermediate synthesis in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. References 2025. Comparative CRISPRi screens reveal a human stem cell dependence on mRNA translation-coupled quality control. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-025-01616-3 2025. pSIG plasmids, MoClo-compatible vectors for efficient production of chimeric double-stranded RNAs in Escherichia coli HT115 (DE3) strain. Plant Methods. DOI: 10.1186/s13007-025-01413-5 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 1-Bromo-3-chloropropane |