Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Hydrocarbon compounds and their derivatives >> Hydrocarbon halide |
|---|---|
| Name | 1-Bromooctane |
| Synonyms | 1-Octylbromide |
| Molecular Structure | 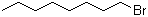 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H17Br |
| Molecular Weight | 193.12 |
| CAS Registry Number | 111-83-1 |
| EC Number | 203-912-9 |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCBr |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 1.118 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | -55 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 200.9±3.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 201 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 78.3 ºC (Calc.)*, 80 ºC (Expl.) |
| Solubility | water: insoluble (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.452 (Calc.)*, 1.452 (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS09 Warning Details
GHS09 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H400-H410 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P391-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1‑Bromooctane is a straight-chain alkyl halide belonging to the class of primary bromoalkanes. Its molecular formula is C8H17Br, and it consists of an eight-carbon linear chain with a bromine atom attached to the terminal carbon. As a primary alkyl bromide, 1‑bromooctane exhibits reactivity typical of primary haloalkanes, including nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions. It is a colorless to pale yellow liquid under standard conditions, with moderate solubility in organic solvents and negligible solubility in water. The compound is primarily used as an intermediate in organic synthesis, particularly in the preparation of long-chain amines, alcohols, ethers, and other functionalized organic molecules. Its bromine atom provides a reactive site for nucleophilic substitution reactions, enabling the introduction of various functional groups while retaining the linear octyl chain. The primary nature of the bromide makes substitution reactions favorable and relatively straightforward, which is advantageous for multi-step synthesis protocols. 1‑Bromooctane is typically synthesized by the free-radical bromination of n-octane or the substitution of 1-octanol with hydrobromic acid or phosphorus tribromide. In the alcohol substitution method, 1-octanol reacts with phosphorus tribromide to replace the hydroxyl group with a bromine atom, forming 1‑bromooctane with high selectivity and yield. Control of temperature and reaction conditions is important to minimize side reactions such as elimination or over-bromination, which can lead to the formation of internal bromoalkanes or polybrominated by-products. Chemically, 1‑bromooctane undergoes nucleophilic substitution through the SN2 mechanism under appropriate conditions. Strong nucleophiles, such as alkoxides, thiolates, and amines, can displace the bromine atom to form ethers, thioethers, or alkylamines, respectively. Because it is a primary bromide, the compound favors SN2 substitution over SN1, leading to minimal carbocation rearrangement. Under strong basic or high-temperature conditions, 1‑bromooctane can undergo elimination reactions to yield octenes, although elimination is less favored compared to secondary or tertiary haloalkanes. 1‑Bromooctane is widely used in pharmaceutical chemistry as an alkylating agent. The octyl chain can impart lipophilicity to drug candidates, improve membrane permeability, or serve as a hydrophobic linker between pharmacophores. In materials science, 1‑bromooctane is used in the synthesis of surfactants, lubricants, and specialty polymers. The terminal bromide provides a reactive site for functionalization, allowing attachment to other molecular fragments or polymer backbones. In addition, it is used in the production of quaternary ammonium salts and other cationic species for use in chemical formulations. From a physical and safety perspective, 1‑bromooctane is volatile and flammable. It should be handled under proper laboratory conditions with gloves, eye protection, and adequate ventilation. The compound is relatively stable under standard storage conditions but can react with strong bases or nucleophiles, as well as with oxidizing agents. Its toxicity is moderate, and exposure can lead to irritation of the skin, eyes, or respiratory system, so care must be taken to avoid direct contact or inhalation of vapors. Overall, 1‑bromooctane is a versatile primary alkyl halide that serves as an important intermediate in organic synthesis. Its linear eight-carbon chain, combined with the reactive bromine atom at the terminal position, allows chemists to construct a wide variety of functionalized molecules, ranging from pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals to surfactants and specialty materials. The balance of reactivity, accessibility, and stability makes 1‑bromooctane a valuable reagent in both laboratory and industrial settings, enabling controlled transformations and selective functionalization in complex synthetic pathways. References 2025. Controlled synthesis of PPV oligomers by ROMP: impact on optical, structural, and thermal properties. Chemical Papers. DOI: 10.1007/s11696-025-04091-8 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 1-Bromooctane |