Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hangzhou Read Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8723-4293 8991-2636 | |||
 |
sales@hzread.com info@hzread.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Changzhou Hangyu Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (519) 8880-2789 +86 13961196887 | |||
 |
sales@czyys.com zypharm78@hotmail.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1984 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Sinfachem Limited | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8468-3399 8517-8591 | |||
 |
sinfachem@foxmail.com sinfachemltd@foxmail.com info@sinfachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Taicang Qianjing Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (512) 5364-5646 | |||
 |
sales@qjchem.com tcqxh@hotmail.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Zhejiang Unipharma-Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8580-3833 | |||
 |
info@unipharma-chem.com chenlinfang@hotmail.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Aromatic aldehyde (containing acetal, hemiacetal) |
|---|---|
| Name | 2-Carboxybenzaldehyde |
| Synonyms | Phthalaldehydic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 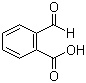 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H6O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 150.13 |
| CAS Registry Number | 119-67-5 |
| EC Number | 204-342-3 |
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C(=C1)C=O)C(=O)O |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 1.404 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 94 - 96 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 321.8±25.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 162.6±19.7 ºC (Calc.)*, 198 ºC (Expl.) |
| Solubility | water: soluble (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.62 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2‑Carboxybenzaldehyde is an aromatic compound characterized by the presence of both an aldehyde group and a carboxylic acid group attached to a benzene ring. In this molecule, the aldehyde functional group is positioned at the first carbon of the benzene ring, and the carboxyl group is attached at the second carbon, giving it an ortho-substituted configuration. Its molecular formula is C8H6O3, and it is a solid under standard conditions with moderate solubility in polar organic solvents and partial solubility in water due to the polar functional groups. The discovery and study of 2‑carboxybenzaldehyde are associated with early research in aromatic aldehydes and carboxylic acids, where chemists sought multifunctional compounds for use in organic synthesis and industrial applications. The ortho relationship between the aldehyde and carboxyl groups provides unique chemical reactivity, particularly in condensation reactions and intramolecular cyclizations. This arrangement allows the molecule to act as a versatile building block for heterocyclic compounds, ligands, and functionalized aromatic systems. Synthesis of 2‑carboxybenzaldehyde is typically achieved by oxidation of 2‑methylbenzoic acid derivatives or through selective formylation of phthalic acid. One common method involves the Vilsmeier-Haack reaction, in which a suitable aromatic precursor is treated with a formylating agent such as the combination of dimethylformamide and phosphorus oxychloride. Alternative synthetic strategies include the oxidation of 2‑hydroxymethylbenzoic acid or ortho-substituted benzyl alcohol derivatives. Controlling reaction conditions is critical to prevent overoxidation or side reactions that could produce the meta or para isomers, which have different chemical properties. Chemically, 2‑carboxybenzaldehyde exhibits the characteristic reactivity of both aldehydes and carboxylic acids. The aldehyde group is highly electrophilic, making it susceptible to nucleophilic attack in reactions such as nucleophilic addition, condensation, and reductive amination. The adjacent carboxyl group can participate in acid-base reactions, esterification, or amide formation. The proximity of the two functional groups enables intramolecular reactions, including the formation of cyclic anhydrides or heterocyclic systems under suitable conditions. This dual reactivity is exploited in organic synthesis to construct complex molecules efficiently. 2‑Carboxybenzaldehyde is widely used as a synthetic intermediate in the preparation of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and coordination ligands. In pharmaceutical chemistry, it serves as a precursor for heterocyclic compounds such as benzofurans, quinolines, and other nitrogen- or oxygen-containing rings. The ability to selectively modify either the aldehyde or carboxyl group allows chemists to introduce functional groups, create linkers, or construct scaffolds for biologically active molecules. Its combination of electrophilicity and acidity makes it a versatile reagent in multistep synthesis. In materials science and chemical research, 2‑carboxybenzaldehyde can be used to prepare metal-chelating ligands, polymer additives, and organic dyes. The ortho arrangement allows chelation to metal centers, which can influence catalytic activity or material properties. The molecule is also employed in condensation reactions to form Schiff bases, imines, or other functionalized compounds used in sensors and supramolecular chemistry. Its solid-state stability and moderate solubility make it convenient to handle in laboratory and industrial settings. From a safety standpoint, 2‑carboxybenzaldehyde should be handled with care. It can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, or respiratory tract upon direct contact or inhalation of dust. Proper protective equipment and ventilation are recommended when working with this compound. Chemically, it is stable under normal storage conditions but should be kept away from strong oxidizing or reducing agents to prevent unwanted reactions. Overall, 2‑carboxybenzaldehyde is a multifunctional aromatic compound that combines an electrophilic aldehyde and an acidic carboxyl group in an ortho-substituted configuration. Its chemical versatility, reactivity, and ability to participate in intramolecular and intermolecular transformations make it a valuable intermediate in organic synthesis, pharmaceutical chemistry, and materials science. The ortho-substitution pattern allows the construction of complex molecules efficiently, and its physical and chemical properties provide ease of handling for laboratory and industrial applications. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 2-Carboxybenzaldehyde |