Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Kangxin Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 6071-2573 | |||
 |
shkangxin@shkangxin.com.cn | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2000 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Suzhou Myland Pharm & Nutrition Inc. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (512) 6615-0687 | |||
 |
info@mylandpharm.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2013 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2014 | ||||
| Chirial Biomaterial Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 19951643840 | |||
 |
cero.xia@chirial.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2020 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Natural Micron Pharm Tech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (0538) 535-2278 | |||
 |
info@nmpharmtech.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Carboxylic compounds and derivatives >> Carboxylic esters and their derivatives |
|---|---|
| Name | Ketone Ester |
| Synonyms | (3R)-3-Hydroxybutanoic acid (3R)-3-hydroxybutyl ester |
| Molecular Structure | 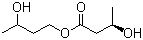 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H16O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 176.21 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1208313-97-6 |
| SMILES | C[C@H](CCOC(=O)C[C@@H](C)O)O |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 268.7±15.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 101.1±13.9 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Solubility | 10 mM (DMSO) (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.461 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS05 Danger Details
GHS05 Danger Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H318 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305+P351+P338+P310 Details |
| Transport Information | UN 1760 |
| SDS | Available |
|
Ketone ester refers to a class of organic compounds in which a ketone body, most commonly derived from hydroxybutyrate or acetoacetate, is chemically esterified to an alcohol. These substances are distinct from simple ketones or dietary ketone salts and have been developed primarily to deliver ketone bodies efficiently into the bloodstream. The discovery and application of ketone esters are closely connected to research on human metabolism, fasting physiology, and the biochemical role of ketone bodies as alternative energy substrates. The scientific background of ketone esters originates in nineteenth-century studies of ketone bodies, which identified acetoacetate, acetone, and hydroxybutyrate as metabolites produced during prolonged fasting or carbohydrate restriction. For much of the twentieth century, ketone bodies were regarded mainly as markers of metabolic stress or disease. However, advances in biochemistry gradually established their role as normal and efficient energy carriers, particularly for the brain, heart, and skeletal muscle during periods of limited glucose availability. This shift in understanding laid the foundation for later efforts to deliver ketone bodies exogenously. Early attempts to raise circulating ketone levels focused on dietary manipulation or the administration of ketone salts. These approaches were limited by gastrointestinal tolerance, mineral load, and modest increases in blood ketone concentrations. The concept of ketone esters emerged from the recognition that esterification could mask the acidity of ketone bodies, improve palatability, and enable higher doses to be consumed. Chemists and physiologists collaborated to design esters that would be rapidly hydrolyzed in vivo, releasing free ketone bodies after absorption. The first systematic development of ketone esters took place in the late twentieth and early twenty-first centuries, driven largely by military and aerospace research. Investigators were interested in metabolic fuels that could sustain cognitive and physical performance under extreme conditions. Ketone esters were identified as promising candidates because they could elevate blood ketone levels without requiring fasting or carbohydrate deprivation. Controlled synthesis of these compounds allowed researchers to study their pharmacokinetics, metabolism, and physiological effects in a reproducible manner. From a chemical perspective, ketone esters are designed so that enzymatic cleavage by esterases yields the desired ketone body and a corresponding alcohol. Once hydrolyzed, the released ketone body enters normal metabolic pathways, being converted to acetyl-CoA and oxidized in the mitochondria. This mechanism enables ketone esters to function as a direct energy source rather than merely a metabolic signal. The chemical stability of the ester bond and the rate of hydrolysis are key factors influencing their effectiveness. Applications of ketone esters have expanded beyond basic research into human metabolism. In sports and exercise science, they have been investigated for their potential to alter substrate utilization, reduce reliance on glycogen, and influence endurance performance. In clinical and translational research, ketone esters have been explored as tools to study neurological metabolism, given the brain’s capacity to utilize ketone bodies efficiently. Their use has also contributed to investigations into metabolic flexibility and the regulation of energy balance. Ketone esters have further played an important role as experimental probes. By allowing precise control over blood ketone concentrations, they have enabled researchers to disentangle the effects of ketones themselves from those of dietary restriction or caloric deficit. This has advanced understanding of ketone signaling, oxidative metabolism, and their interactions with glucose and fatty acid pathways. In summary, ketone esters represent a chemically engineered solution to delivering ketone bodies in a controlled and efficient manner. Their discovery was driven by evolving insights into ketone metabolism, and their applications span fundamental physiology, performance research, and metabolic science. Rather than serving as simple nutrients, ketone esters function as specialized research and nutritional tools that have significantly deepened scientific understanding of human energy metabolism. References 2025. Characterizing the Hepatic Metabolic Pathway of Ketone Ester and Subsequent Metabolites Using Human and Rat Liver Fractions. The AAPS Journal. DOI: 10.1208/s12248-025-01044-7 2025. Heart ketone metabolism under acute ketone supplementation in ZDF rats, a type 2 diabetes heart failure model. EJNMMI Research. DOI: 10.1186/s13550-025-01215-9 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Ketone Ester |