Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Amide |
|---|---|
| Name | N-Bromosuccinimide |
| Synonyms | Bromosuccinimide; Succinbromimide; 1-Bromo-2,5-pyrrolidinedione |
| Molecular Structure | 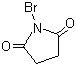 |
| Molecular Formula | C4H4BrNO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 177.98 |
| CAS Registry Number | 128-08-5 |
| EC Number | 204-877-2 |
| SMILES | C1CC(=O)N(C1=O)Br |
| Density | 2.0±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 2.098 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 175 - 180 ºC (Decomposes) (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 221.4±23.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 87.7±22.6 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.606 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |




 GHS03;GHS05;GHS07;GHS08;GHS09 DangerGHS05 Details
GHS03;GHS05;GHS07;GHS08;GHS09 DangerGHS05 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H272-H290-H302-H314-H315-H317-H319-H335-H341-H400 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P203-P210-P220-P234-P260-P261-P264-P264+P265-P270-P271-P272-P273-P280-P301+P317-P301+P330+P331-P302+P352-P302+P361+P354-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P305+P354+P338-P316-P318-P319-P321-P330-P332+P317-P333+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P363-P370+P378-P390-P391-P403+P233-P405-P406-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
N‑Bromosuccinimide, commonly abbreviated as NBS, is an organobromine compound widely used as a brominating and oxidizing reagent in organic synthesis. Its chemical formula is C4H4BrNO2, and its structure consists of a succinimide ring with a bromine atom attached to the nitrogen atom. NBS is a white to off-white crystalline solid that is moderately soluble in water and highly soluble in polar organic solvents such as carbon tetrachloride, chloroform, and dimethylformamide. The compound is notable for its ability to provide a controlled source of bromine under mild conditions, making it a versatile tool for chemists. The discovery and application of NBS date back to the mid-20th century when chemists sought reagents capable of performing selective bromination without the use of elemental bromine, which is highly volatile and corrosive. NBS was found to act as a stable solid brominating agent, releasing bromine slowly in situ under reaction conditions. This property allows for greater control over bromination reactions and reduces side reactions and overbromination compared to direct use of molecular bromine. Its combination of stability, selectivity, and ease of handling quickly established NBS as a staple reagent in laboratories. NBS is primarily used for allylic and benzylic bromination reactions. The compound generates small amounts of bromine radical in the presence of light, heat, or radical initiators such as azobisisobutyronitrile. These radicals selectively abstract hydrogen atoms from allylic or benzylic positions, forming carbon-centered radicals that then react with bromine to yield the corresponding brominated product. This method allows chemists to perform bromination with high regioselectivity and minimal formation of polybrominated by-products. NBS can also participate in other radical-based reactions and can be used for bromohydrin formation in the presence of water. In addition to radical bromination, NBS is employed in electrophilic bromination of electron-rich aromatic and heteroaromatic compounds. Under acidic or neutral conditions, the nitrogen-bonded bromine can transfer to nucleophilic sites on the substrate, introducing bromine into the aromatic ring. This electrophilic reaction is widely used in the preparation of halogenated intermediates for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and dyes. NBS is preferred over elemental bromine in these contexts because it allows for precise stoichiometric control, minimizing excessive halogenation. NBS is also used as an oxidizing agent in specific transformations. For example, it can facilitate the conversion of alcohols to carbonyl compounds, the formation of halohydrins from alkenes, or oxidative cyclizations in heterocyclic synthesis. Its versatility stems from the ability of the N–Br bond to act as both a radical and an electrophilic bromine source, depending on the reaction environment. This dual functionality makes NBS a highly adaptable reagent for both academic research and industrial chemistry applications. From a physical and safety perspective, NBS is stable under dry, cool storage but is sensitive to light and moisture, which can promote slow decomposition and release of bromine. Proper handling requires storage in tightly sealed containers, away from direct sunlight and strong reducing agents. Contact with combustible materials or strong acids should be avoided. NBS can cause skin and eye irritation, and inhalation of dust should be prevented, so personal protective equipment and adequate ventilation are recommended. Overall, N‑bromosuccinimide is a chemically versatile organobromine reagent that provides a controlled source of bromine for radical and electrophilic reactions. Its stability, selectivity, and ease of use have made it indispensable in organic synthesis, from laboratory-scale transformations to industrial applications. By combining radical and electrophilic bromination capabilities with mild reaction conditions, NBS remains a fundamental tool for chemists seeking efficient and selective halogenation of organic molecules. References 2025. Decarboxylative bromination and chlorination of carboxylate salts: from discovery (Alexander Borodin, 1861) to development of a synthetic methodology (Cl�re and Heinz Hunsdiecker, 1935�1942) and present perspectives of the reaction. Chemical Papers. DOI: 10.1007/s11696-025-04077-6 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for N-Bromosuccinimide |