Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Zhejiang Yangfan New Materials Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8890-2510 8890-2504 8890-2511 | |||
 |
shoufu@shoufuchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| Tyger Scientific Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (609) 434-0144 | |||
 |
sales@tygersci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1992 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Hangzhou TJM Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13388471767 | |||
 |
sales@tjmchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Auben Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 19121901603 | |||
 |
sales@aubenchem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2023 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Flavors and spices >> Synthetic spice >> Thioether perfume |
|---|---|
| Name | Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)disulfide |
| Synonyms | 4,4'-Dithiodiphenol |
| Molecular Structure | 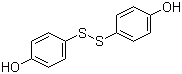 |
| Molecular Formula | C12H10O2S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 250.34 |
| CAS Registry Number | 15015-57-3 |
| EC Number | 805-758-3 |
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1O)SSC2=CC=C(C=C2)O |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 152 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 437.9±30.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 212.5±23.3 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.752 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS07;GHS09 Warning Details
GHS07;GHS09 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335-H400-H410 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P270-P271-P273-P280-P301+P317-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P330-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P391-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Bis(4‑hydroxyphenyl)disulfide is an organosulfur compound characterized by two hydroxyphenyl groups linked through a disulfide bond. Its molecular formula is C12H10O2S2. The molecule contains two aromatic rings substituted at the para position with hydroxyl groups, connected via a central –S–S– linkage. The presence of the hydroxyl groups contributes to hydrogen bonding, polarity, and solubility in polar solvents, while the disulfide bond provides unique redox and chemical reactivity. Under standard conditions, bis(4‑hydroxyphenyl)disulfide appears as a yellow to orange crystalline solid. The discovery and application of bis(4‑hydroxyphenyl)disulfide are closely tied to research into disulfide-containing aromatic compounds. These compounds are valued for their role in redox chemistry, polymer stabilization, and as intermediates in organic synthesis. The disulfide bond is capable of reversible cleavage under reducing conditions, allowing the compound to participate in electron transfer and radical reactions. This property has made it useful in the design of antioxidants, vulcanization accelerators, and redox-active materials. Synthesis of bis(4‑hydroxyphenyl)disulfide is generally achieved through oxidation of 4‑mercaptophenol. The thiol functional group of 4‑mercaptophenol is converted into a disulfide by treatment with mild oxidizing agents such as iodine, hydrogen peroxide, or oxygen under controlled conditions. This reaction selectively couples two thiol molecules to form the disulfide without affecting the hydroxyl groups. Alternative methods include air oxidation in basic aqueous solutions or catalyzed oxidative coupling reactions. Reaction conditions such as pH, temperature, and solvent choice are carefully controlled to maximize yield and purity. Chemically, bis(4‑hydroxyphenyl)disulfide exhibits reactivity typical of both phenolic and disulfide functional groups. The hydroxyl groups can undergo esterification, etherification, and electrophilic aromatic substitution, providing sites for further chemical modification. The disulfide bond is sensitive to reducing agents, which can cleave it to yield two molecules of 4‑hydroxythiophenol. Conversely, the disulfide can be oxidized further under strong oxidative conditions, allowing the formation of sulfonic acids or other oxidized sulfur species. This dual redox activity makes bis(4‑hydroxyphenyl)disulfide a versatile reagent in organic synthesis and materials chemistry. In applied chemistry, bis(4‑hydroxyphenyl)disulfide is used as a precursor for polymers and crosslinking agents. Its ability to form reversible disulfide bonds allows incorporation into polymer backbones for stimuli-responsive materials. These materials can undergo cleavage or rearrangement under reducing conditions, providing dynamic properties in coatings, adhesives, and hydrogels. Additionally, the phenolic groups can participate in hydrogen bonding or chemical functionalization, further expanding the range of applications. In the field of pharmaceuticals and biochemistry, disulfide compounds such as bis(4‑hydroxyphenyl)disulfide are studied for antioxidant properties and interactions with thiol-containing biomolecules. The compound’s ability to undergo reversible redox reactions allows it to act as a stabilizer in formulations or as a model compound in studies of disulfide exchange reactions. Its moderate solubility in polar organic solvents facilitates laboratory handling and incorporation into chemical reactions. From a safety perspective, bis(4‑hydroxyphenyl)disulfide should be handled with care. It may cause skin and eye irritation, and dust inhalation should be avoided. The compound is chemically stable under ambient conditions but can react with strong oxidizing or reducing agents, depending on the desired chemical transformation. Proper storage in a dry, cool environment is recommended to maintain its stability and prevent unwanted decomposition. Overall, bis(4‑hydroxyphenyl)disulfide is a multifunctional organosulfur compound combining aromatic hydroxyl groups with a reactive disulfide linkage. Its chemical versatility, including phenolic reactivity and reversible redox behavior, makes it a valuable intermediate for synthesis, polymer chemistry, and redox studies. Its structural features and functional properties continue to support applications in material design, chemical research, and industrial chemistry. References 2024. Room-temperature Self-healing and Recyclable PDMS Elastomers with Superior Mechanical Properties for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science. DOI: 10.1007/s10118-024-3178-5 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)disulfide |