Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| RC Chemicals Lab Inc | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (401) 232-4508 | |||
 |
info@rcchemicallabs.net | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Pyrimidine compound >> Urinary (urea) pyrimidine |
|---|---|
| Name | 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil |
| Synonyms | 5-A-RU |
| Molecular Structure | 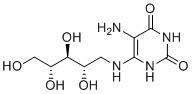 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H16N4O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 276.25 |
| CAS Registry Number | 17014-74-3 |
| SMILES | C([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](CO)O)O)O)NC1=C(C(=O)NC(=O)N1)N |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Index of refraction | 1.676 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
|
5-Amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil is a naturally occurring biochemical intermediate that plays a key role in the biosynthesis of riboflavin (vitamin B2). Its discovery is linked to studies of microbial riboflavin metabolism conducted in the mid to late twentieth century, when the enzymatic pathways for flavin biosynthesis were being elucidated. Researchers identified that bacteria and fungi convert GTP and ribulose-5-phosphate into riboflavin via a series of enzymatic steps, one of which involves the formation of 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil as a central intermediate. Structurally, 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil consists of a uracil base modified at the 6-position with a D-ribitylamino substituent and an amino group at the 5-position. This configuration enables the molecule to undergo subsequent enzymatic transformations, including condensation with 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate to form 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine, which is then converted to riboflavin by lumazine synthase and riboflavin synthase. Its reactivity stems from the electron-rich amino and ribitylamino groups, which participate in nucleophilic addition and rearrangement reactions during these biosynthetic steps. The compound was first characterized through a combination of enzymatic assays, chromatographic separation, and spectroscopic analysis. Studies showed that microbial extracts capable of riboflavin synthesis accumulate 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil when specific enzyme activities are inhibited or when the pathway is stalled at intermediate steps. These experiments confirmed its role as a true intermediate rather than a side product. In terms of application, 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil is primarily important in microbiology, biochemistry, and metabolic engineering. Understanding its formation and conversion has enabled the development of riboflavin-overproducing bacterial strains for industrial vitamin production. Additionally, the compound is used as a substrate in in vitro studies of flavin biosynthetic enzymes to elucidate reaction mechanisms, enzyme kinetics, and substrate specificity. Structural analogues have also been employed to probe enzyme active sites and to investigate inhibition strategies for potential antimicrobial development targeting flavin biosynthesis. From a chemical standpoint, the compound’s stability is sufficient for laboratory handling under controlled conditions, although it is typically prepared enzymatically or isolated from microbial cultures rather than by purely chemical synthesis. It is water-soluble and participates in specific enzyme-catalyzed reactions without the need for protective groups or derivatization in standard assays. Overall, 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil represents a well-characterized intermediate in riboflavin biosynthesis. Its identification, characterization, and enzymatic applications have contributed substantially to our understanding of flavin metabolism and have provided a foundation for both industrial and academic research in vitamin B2 production. References Fischer M and Bacher A (2005) Biosynthesis of flavocoenzymes. Natural Product Reports 22 3 324–350 DOI: 10.1039/B210142B Harzer G, Rokos H, Otto MK, Bacher A, Ghisla S (1978) Biosynthesis of riboflavin. 6,7‑dimethyl‑8‑ribityllumazine 5’‑phosphate is not a substrate for riboflavin synthase. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 540(1) 48–54 DOI: 10.1016/0304‑4165(78)90433‑6 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil |