Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Beijing Acemol Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (10) 6970-1569 | |||
 |
sales@acemol.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2015 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Amadis Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8992-5085 | |||
 |
sales@amadischem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Auben Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 19121901603 | |||
 |
sales@aubenchem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2023 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Synthonix, Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (919) 875-9277 | |||
 |
info@synthonix.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Ketone compound |
|---|---|
| Name | 3-(Hydroxymethyl)cyclobutanone |
| Molecular Structure | 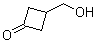 |
| Molecular Formula | C5H8O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 100.12 |
| CAS Registry Number | 183616-18-4 |
| EC Number | 809-953-4 |
| SMILES | C1C(CC1=O)CO |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 204.7±13.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 80.6±12.4 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.488 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H332-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P317-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
3-(Hydroxymethyl)cyclobutanone is a small cyclic ketone containing a four-membered cyclobutanone ring substituted at the third carbon with a hydroxymethyl group. Its molecular formula is C5H8O2, and it exists as a colorless to pale yellow liquid or solid depending on conditions. The compound combines the chemical reactivity of a strained cyclobutanone ring with that of a primary alcohol, allowing it to participate in diverse organic reactions. The four-membered ring introduces ring strain that increases the reactivity of the carbonyl group compared with larger cyclic ketones, while the hydroxymethyl substituent contributes to hydrogen bonding, solubility in polar organic solvents, and versatility in functional group transformations. The discovery of 3-(hydroxymethyl)cyclobutanone is part of broader research into cyclobutanone derivatives and strained-ring compounds. Cyclobutanones are valued for their increased reactivity due to angle strain in the four-membered ring, which facilitates reactions such as nucleophilic addition, condensation, and ring-opening. The hydroxymethyl substitution provides an additional functional handle for derivatization, enabling chemists to attach protective groups, convert the alcohol into other functional groups, or link it to larger molecular scaffolds. These features make the compound particularly useful as a synthetic intermediate. Synthesis of 3-(hydroxymethyl)cyclobutanone can be achieved by multiple methods. One common approach involves hydroxymethylation of cyclobutanone using formaldehyde under basic or acidic conditions, forming the desired alcohol at the third carbon. Alternative strategies include [2+2] cycloaddition reactions of ketenes or α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds with alkenes, followed by functionalization at the 3-position. Protecting groups may be temporarily introduced to the hydroxyl functionality during multistep syntheses to prevent side reactions, with subsequent deprotection yielding the free hydroxymethyl group. Chemically, 3-(hydroxymethyl)cyclobutanone exhibits dual reactivity due to the presence of both the ketone and alcohol functional groups. The carbonyl group can undergo nucleophilic addition, reduction, or condensation reactions, while the hydroxyl group can participate in esterification, ether formation, or oxidation. The ring strain enhances the reactivity of the carbonyl group, allowing reactions that may be sluggish in larger ring systems. This combination of functionalities makes the compound a versatile intermediate for the preparation of complex molecules. Applications of 3-(hydroxymethyl)cyclobutanone include its use as a building block for the synthesis of more complex carbocyclic compounds, heterocycles, and natural product analogues. Its hydroxymethyl group can be derivatized to introduce protecting groups or linkers for further functionalization, while the cyclobutanone core can undergo ring-expansion, ring-opening, or rearrangement reactions to access structurally diverse products. These characteristics make it valuable in medicinal chemistry, synthetic organic chemistry, and materials research. From a physical standpoint, 3-(hydroxymethyl)cyclobutanone is moderately soluble in polar organic solvents such as acetone, ethanol, and dimethyl sulfoxide. The strained ring system and the hydroxymethyl group influence its melting point, boiling point, and crystallization behavior. The compound is generally stable under ambient conditions but should be stored in cool, dry environments to avoid decomposition or polymerization. Handling precautions include avoiding inhalation of vapors and contact with skin or eyes, as the compound can be an irritant. Overall, 3-(hydroxymethyl)cyclobutanone is a multifunctional small-ring ketone with broad synthetic utility. Its combination of a strained cyclobutanone core and a reactive hydroxymethyl substituent enables selective chemical transformations for the construction of diverse organic molecules. The compound’s chemical versatility, functional group compatibility, and ring strain make it an important intermediate in synthetic strategies, supporting applications in medicinal chemistry, natural product synthesis, and advanced materials design. References 2025. Compounds and methods of treating cancers. WO Patent. URL: WO-2025103502-A1 2024. Bifunctional degraders and uses thereof. WO Patent. URL: WO-2024249291-A2 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 3-(Hydroxymethyl)cyclobutanone |