Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Nanjing Search Biotech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8168-2922 8586-0978 +86 18913919581 | |||
 |
trade@searchbio.com.cn sales@searchbio.com.cn Linda@searchbio.com.cn | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Survival Technologies Pvt Ltd | India | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+91 (22) 4212-8221 | |||
 |
info@survivaltechnologies.in | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Beijing Mesochem Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (10) 5786-2036 57862181 67374028 +86 13366977697 | |||
 |
sales@mesochem.com huafenginfo@126.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Primarius Custom Synthesis P. Ltd. | India | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+91 (265) 233-1730 | |||
 |
info@primariusfinechem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1999 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Hangzhou TJM Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13388471767 | |||
 |
sales@tjmchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Niche Materials Ltd | UK | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+44 (7770) 983-290 | |||
 |
enzo.costa@nichematerials.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| LOBA Feinchemie AG | Austria | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+43 (223) 277-391 | |||
 |
sales@loba.co.at | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Classification | Analytical chemistry >> Analytical reagent >> Common analytical reagents |
|---|---|
| Name | 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride |
| Synonyms | 2,3,5-Triphenyl-2H-tetrazolium chloride; Tetrazolium Red |
| Molecular Structure | 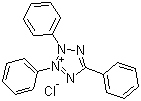 |
| Molecular Formula | C19H15N4.Cl |
| Molecular Weight | 334.81 |
| CAS Registry Number | 298-96-4 |
| EC Number | 206-071-6 |
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=NN([N+](=N2)C3=CC=CC=C3)C4=CC=CC=C4.[Cl-] |
| Melting point | 250 ºC (Decomposes) (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS02;GHS07 DangerGHS02 Details
GHS02;GHS07 DangerGHS02 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H228-H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P240-P241-P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P370+P378-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) is an organic compound belonging to the tetrazolium salts, characterized by a tetrazole ring substituted with three phenyl groups and a chloride counterion. Its molecular formula is C19H15ClN4. TTC is a red or orange crystalline solid under standard conditions and is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents. The tetrazolium core contains a four-nitrogen ring system capable of undergoing reduction reactions, which is the basis for its chemical reactivity and widespread use in biochemical assays. The discovery and application of TTC are closely linked to its role as a redox indicator in biological systems. Tetrazolium salts were first explored for their ability to accept electrons from enzymatic or cellular metabolic activity, producing colored formazan products. TTC, in particular, has been widely used to assess cell viability and mitochondrial function because it is colorless in its oxidized form but is converted to a red, insoluble triphenyl formazan upon reduction. This property allows direct visual detection of metabolic activity in cells, tissues, or microbial cultures. Synthesis of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride generally involves the condensation of triphenylmethyl derivatives with sodium azide under acidic or neutral conditions to form the tetrazole ring, followed by formation of the chloride salt through protonation or ion exchange. The reaction is conducted under controlled temperature to avoid decomposition of the tetrazole ring and to ensure high yield of the chloride salt. The final product is typically purified by recrystallization from water or ethanol to remove unreacted starting materials and by-products. Chemically, TTC is highly reactive toward reducing agents due to the electron-deficient tetrazole ring. The compound undergoes one-electron or two-electron reduction, producing triphenylformazan, a colored and insoluble compound. This reduction is catalyzed by enzymes such as dehydrogenases in living cells, which transfer electrons from substrates to TTC. The conversion is quantitative and proportional to the metabolic activity, making TTC a reliable reagent for cell viability assays, enzymatic activity studies, and microbial growth detection. In practical applications, 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride is extensively used in microbiology, biochemistry, and plant physiology. In microbiology, it serves as an indicator of bacterial or fungal metabolic activity in culture. In plant physiology, TTC staining is employed to assess seed viability and germination by revealing living tissues capable of reducing TTC. In biochemical assays, the compound can monitor mitochondrial respiration and enzymatic activity in vitro, providing a convenient and sensitive colorimetric method for detecting living cells or active enzymes. Physically, TTC is stable under dry, ambient conditions but should be protected from strong reducing agents and prolonged light exposure, which can lead to premature conversion to formazan. Its crystalline nature facilitates storage and handling, and it can be dissolved in aqueous buffer solutions or alcohols for experimental use. Standard safety precautions include avoiding inhalation or skin contact, as tetrazolium salts may cause irritation. Overall, 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride is a chemically stable tetrazolium salt with a versatile role as a redox indicator in biological and biochemical research. Its reduction to colored formazan products allows visualization and quantification of cellular metabolic activity, making it an important tool in cell viability studies, microbial detection, and enzymatic assays. The compound’s combination of chemical reactivity, stability, and colorimetric response underlies its widespread use in laboratory and research applications. References 2025. Insights Into the Enhanced Biodegradation of Pyrene Under Glucose Co-Metabolism. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution. DOI: 10.1007/s11270-025-08338-8 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride |