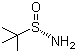
(S)-tert-Butylsulfinamide is an organosulfur compound consisting of a tert-butyl group attached to a sulfinamide functional group, with defined (S)-stereochemistry at the sulfur atom. Its molecular formula is C4H11NOS. The compound appears as a colorless crystalline solid and is soluble in polar organic solvents such as dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, and ethanol, while exhibiting limited solubility in water. The chiral sulfinamide moiety provides both nucleophilic and electrophilic reactivity, making it a versatile building block in asymmetric synthesis.
The discovery of (S)-tert-butylsulfinamide is tied to the development of chiral auxiliaries and chiral amine synthesis. Sulfinamides were recognized for their ability to induce stereocontrol in nucleophilic addition reactions due to the stereogenic sulfur atom. The tert-butyl group imparts steric bulk that enhances diastereoselectivity during reactions with carbonyl compounds, imines, and electrophiles. As a result, (S)-tert-butylsulfinamide is widely used as a chiral auxiliary to produce enantiomerically enriched amines and other nitrogen-containing compounds.
Synthesis of (S)-tert-butylsulfinamide typically involves oxidation of tert-butylthiol or tert-butylsulfide derivatives to generate the corresponding sulfinyl chloride, followed by reaction with ammonia or an amine source under controlled conditions to form the sulfinamide. Enantioselective oxidation or resolution strategies are employed to obtain the (S)-enantiomer with high optical purity. Purification is generally accomplished by recrystallization from suitable organic solvents, yielding a stable, stereochemically defined product.
Chemically, (S)-tert-butylsulfinamide exhibits nucleophilic behavior at the nitrogen atom and electrophilic behavior at the sulfur center. The sulfur atom is stereogenic, allowing it to direct stereoselective reactions, particularly in the formation of imines and subsequent nucleophilic additions. The tert-butyl group shields one face of the sulfinamide, enabling high diastereoselectivity when reacting with prochiral electrophiles. The compound is stable under ambient conditions but can undergo oxidation to the corresponding sulfonamide or reduction to the corresponding thiol under appropriate conditions.
In organic synthesis, (S)-tert-butylsulfinamide is primarily employed as a chiral auxiliary in the asymmetric synthesis of amines, including α-amino acids, alkaloids, and pharmaceutical intermediates. It can form N-sulfinyl imines with aldehydes or ketones, which then undergo stereoselective nucleophilic addition to produce enantiomerically enriched amines after deprotection. This strategy allows precise control over absolute configuration and has been applied in the synthesis of complex molecules for medicinal chemistry.
From a physical perspective, the compound is thermally stable and can be handled under normal laboratory conditions. It is typically stored in tightly sealed containers to avoid moisture, which may affect its crystalline structure or lead to hydrolysis. Standard laboratory safety procedures, including gloves and eye protection, should be followed when handling, as it is an irritant to skin and eyes.
Overall, (S)-tert-butylsulfinamide is a chiral organosulfur compound of significant importance in asymmetric synthesis. Its stereogenic sulfur atom, combined with the steric influence of the tert-butyl group, enables the production of enantiomerically enriched amines with high selectivity. The compound serves as a cornerstone reagent in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, natural products, and complex nitrogen-containing molecules, exemplifying the utility of chiral sulfinamides in modern organic chemistry.
References
2024. A comprehensive review on synthetic strategy and MOA of marketed drugs having therapeutically potential chemical entity pyrazole. Journal of the Iranian Chemical Society.
DOI: 10.1007/s13738-024-03095-7
|

















 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details