Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Zhengzhou Kingsfine Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (371) 5663-2527 +86 13838252817 | |||
 |
sales@kingsfine.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13838252817 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2011 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Shanghai Scientia Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 5430-1573 6172-1573 400-036-1573 | |||
 |
sales@scientiapharm.com scientiapharm@gmail.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Forxine Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 6496-1699 | |||
 |
reagent@forxine.com sales@forxine.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2013 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2014 | ||||
| Viwit Pharmaceuticals Limited | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 3777-5618 | |||
 |
service@viwit.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2016 | ||||
| Shanghai Yingrui Biopharm Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 3358-5366 3466-6753 +86 13311639313 | |||
 |
sales02@shyrchem.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2017 | ||||
| Auben Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 19121901603 | |||
 |
sales@aubenchem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2023 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Strem Chemicals, Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (978) 499-1600 | |||
 |
info@strem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Borane |
|---|---|
| Name | tert-Butylamine borane |
| Molecular Structure | 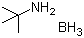 |
| Molecular Formula | C4H11N.BH3 |
| Molecular Weight | 86.97 |
| CAS Registry Number | 7337-45-3 |
| EC Number | 230-851-5 |
| SMILES | [B].CC(C)(C)N |
| Melting point | 96-101 ºC (dec.) |
|---|---|
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS06;GHS09 Danger Details
GHS06;GHS09 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H301+H311,H315,H319,H411 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P273-P280-P301+P310-P302+P352+P312-P305+P351+P338 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 2811 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
tert-Butylamine borane is an organoboron compound consisting of a tert-butylamine moiety coordinated to a borane (BH3) group, forming a stable adduct. Its molecular formula is C4H13NB. The compound is typically a colorless to pale yellow solid or crystalline material that is soluble in polar organic solvents such as tetrahydrofuran, ethanol, or dichloromethane. The adduct formation between the tertiary amine and borane stabilizes the reactive BH3 unit, allowing safer handling compared to free borane. The discovery and development of amine-borane adducts, including tert-butylamine borane, stem from the need for stable, easily handled sources of borane for use in organic synthesis and reduction chemistry. Borane itself is highly reactive and pyrophoric, but coordination to a Lewis base such as tert-butylamine produces a solid or liquid complex that retains the reducing properties of BH3 while being much safer to store and handle. These adducts have been extensively studied since the mid-20th century for applications in hydroboration, reduction, and hydrogen storage. Synthesis of tert-butylamine borane is typically performed by direct reaction of tert-butylamine with borane in an inert solvent under controlled conditions. A common method involves bubbling diborane (B2H6) or using a commercially available borane–tetrahydrofuran solution into a cooled solution of tert-butylamine. The reaction proceeds spontaneously with the formation of a stable dative bond between the nitrogen lone pair and the boron atom. The product can be isolated by crystallization or distillation under reduced pressure to remove unreacted reagents and solvent. Chemically, tert-butylamine borane functions as a mild and selective reducing agent due to the BH3 moiety. The boron atom can transfer hydride ions to electrophilic centers such as carbonyl compounds, imines, and certain unsaturated systems, resulting in the reduction of ketones, aldehydes, and imines to the corresponding alcohols or amines. The sterically bulky tert-butyl group provides some protection to the boron, modulating its reactivity compared to less hindered amine-borane adducts. The compound is stable under dry, inert conditions but can release hydrogen or decompose upon exposure to moisture, acids, or high temperatures. In practical applications, tert-butylamine borane is employed in organic synthesis as a selective reducing agent for the reduction of aldehydes, ketones, and imines under mild conditions. Its stability and ease of handling make it suitable for laboratory-scale reactions, particularly when controlled delivery of borane is required. In addition, tert-butylamine borane and related amine-borane adducts are studied as potential hydrogen storage materials due to their high hydrogen content and ability to release hydrogen upon thermal or catalytic activation. Physically, the compound is generally stable when stored as a solid in airtight containers under an inert atmosphere, away from moisture and heat. Handling precautions include gloves, eye protection, and proper ventilation, as exposure to water or acids can release flammable hydrogen gas. It is also sensitive to strong oxidizers and should be stored away from reactive chemicals. Overall, tert-butylamine borane is a useful organoboron compound that combines the reducing power of BH3 with the stability imparted by a bulky amine. Its controlled reactivity, ease of handling, and versatility in reduction reactions make it a valuable reagent in synthetic organic chemistry, with potential applications in hydrogen storage and related fields. References 2016. Novel stereoselective bufadienolides reveal new insights into the requirements for Na(+), K(+)-ATPase inhibition by cardiotonic steroids. Scientific Reports. DOI: 10.1038/srep29155 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for tert-Butylamine borane |