Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Nanjing Search Biotech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8168-2922 8586-0978 +86 18913919581 | |||
 |
trade@searchbio.com.cn sales@searchbio.com.cn Linda@searchbio.com.cn | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Discovery Fine Chemicals Ltd. | UK | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+44 (1202) 874-517 | |||
 |
pjc@discofinechem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Shaoxing Echem Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (575) 8676-6255 +86 15305756276 | |||
 |
echem2009@hotmail.com david.dai@sensechemicals.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Ereztech LLC | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (888) 658-1221 | |||
 |
sales@ereztech.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Apexbio Technology LLC | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (832) 696-8203 | |||
 |
info@apexbt.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2013 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Amino compound >> Sulfonic acid amino compound |
|---|---|
| Name | 3-((3-Cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonium)-1-propanesulfonate |
| Synonyms | CHAPS |
| Molecular Structure | 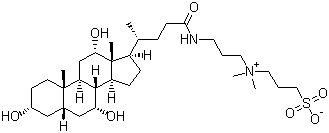 |
| Molecular Formula | C32H58N2O7S |
| Molecular Weight | 614.88 |
| CAS Registry Number | 75621-03-3 |
| EC Number | 616-246-2 |
| SMILES | C[C@H](CCC(=O)NCCC[N+](C)(C)CCCS(=O)(=O)[O-])[C@H]1CC[C@@H]2[C@@]1([C@H](C[C@H]3[C@H]2[C@@H](C[C@H]4[C@@]3(CC[C@H](C4)O)C)O)O)C |
| Solubility | Water: 45mg/mL, DNSO: 10 mM (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
3-((3-Cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonium)-1-propanesulfonate, commonly known as CHAPS, is a zwitterionic detergent widely used in biochemistry and molecular biology for solubilizing membrane proteins while maintaining their native structure. Its molecular formula is C32H58N2O7S. Structurally, CHAPS contains a steroidal cholamide backbone linked to a dimethylammonium-propane unit and a propanesulfonate group, giving it both a hydrophobic and hydrophilic region. This amphiphilic design allows it to interact with lipid bilayers without denaturing proteins. It typically appears as a white to off-white crystalline powder that is soluble in water and polar solvents, forming clear solutions at concentrations above its critical micelle concentration (CMC). The development of CHAPS stems from the need for mild detergents capable of solubilizing integral membrane proteins without disrupting their tertiary or quaternary structures. Traditional ionic detergents like SDS often denature proteins, while nonionic detergents may be insufficient for solubilization. CHAPS, first reported in the late 1970s, combines the zwitterionic properties of sulfobetaines with a rigid steroidal backbone, providing a detergent that is effective yet minimally denaturing. Its zwitterionic nature allows it to reduce protein aggregation and maintain functional conformations. Synthesis of CHAPS involves derivatization of cholic acid, a naturally occurring bile acid, to introduce an amide linkage to a 3-dimethylaminopropyl group. This is followed by quaternization of the amine with methyl halides to form the permanent dimethylammonium group. Finally, the propanesulfonate moiety is introduced to balance the cationic ammonium group, creating the zwitterionic structure. Purification is typically carried out through recrystallization or chromatography to remove unreacted intermediates and by-products. The resulting compound is stable and suitable for use in aqueous solutions for biochemical applications. Chemically, CHAPS is amphiphilic, containing both hydrophilic and hydrophobic domains. The steroidal portion interacts with lipid bilayers, while the sulfonate and ammonium groups interact with aqueous environments. This allows CHAPS to form micelles at relatively low concentrations, effectively solubilizing membrane proteins while preserving their functional and structural integrity. It is non-denaturing, non-oxidizing, and compatible with many biochemical assays, making it a preferred choice for studies involving sensitive proteins. In practical applications, CHAPS is extensively used in membrane protein extraction, purification, and crystallization. It is applied in protein solubilization for electrophoresis, enzymatic assays, and structural biology studies, including X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy. Its mild nature ensures that proteins retain biological activity, which is critical for functional studies. Additionally, CHAPS is used in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and other proteomics techniques to improve protein resolution. Physically, CHAPS is stable at room temperature and can be stored as a solid or in aqueous solution. Solutions should be protected from contamination and extreme pH to maintain detergent integrity. Standard laboratory precautions, including gloves and eye protection, are recommended when handling powders or concentrated solutions. Overall, 3-((3-Cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonium)-1-propanesulfonate (CHAPS) is a zwitterionic steroidal detergent that plays a critical role in membrane protein biochemistry. Its combination of amphiphilic structure, mild non-denaturing properties, and effective micelle formation makes it an essential tool for protein solubilization, purification, and structural analysis in modern biochemical research. References 2025. Transplantation of miR-216a-5p-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in a thermosensitive hydrogel promotes functional recovery in a rat model of spinal cord injury. European Journal of Medical Research. DOI: 10.1186/s40001-025-02860-5 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 3-((3-Cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonium)-1-propanesulfonate |