Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Chengdu Youngshe Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (28) 6232-8193 +86 17380623303 | |||
 |
caroline@youngshechem.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2013 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Nanjing Leon Biological Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8452-3390 ex 127 | |||
 |
sales@njleonbiotech.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2014 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Chengdu Jinglin Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 17380623303 | |||
 |
yunxicaroline@gmail.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2021 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2022 | ||||
| Aajiang Jiuzhou Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13454675544 | |||
 |
jamie@jiuzhou-chem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: +86 18632988332 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 18632988332 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Natural Micron Pharm Tech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (0538) 535-2278 | |||
 |
info@nmpharmtech.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Biochemical >> Peptide |
|---|---|
| Name | N2-Acetyl-L-lysylglycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysinamide |
| Molecular Structure | 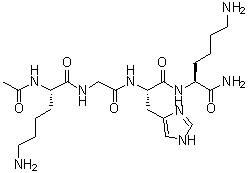 |
| Protein Sequence | KGHK |
| Molecular Formula | C22H39N9O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 509.60 |
| CAS Registry Number | 827306-88-7 |
| SMILES | CC(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H](CC1=CN=CN1)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N |
| Solubility | Freely soluble (150 g/L) (25 ºC), Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.250±0.06 g/cm3 (20 ºC 760 Torr), Calc.* |
| Boiling point | 1075.4±65.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 604.2±34.3 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.562 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
|
N2-Acetyl-L-lysylglycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysinamide is a synthetic oligopeptide composed of four amino acid residues with defined stereochemistry and terminal modifications. The molecule contains an N2-acetylated lysine residue at the amino terminus, followed by glycine, histidine, and a C-terminal lysinamide. Such structural features place the compound within a class of deliberately engineered peptides designed for stability, controlled charge distribution, and specific biochemical behavior. Its significance arises from advances in peptide chemistry and the systematic exploration of short peptide sequences in biological research. The discovery of peptides like N2-acetyl-L-lysylglycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysinamide is closely associated with the maturation of peptide synthesis techniques in the mid to late twentieth century. The development of solid-phase peptide synthesis made it possible to assemble short peptides rapidly and with high precision. Researchers were no longer limited to naturally occurring sequences and began constructing modified peptides to study the influence of individual amino acids, terminal capping groups, and side-chain functionalities. Within this context, peptides incorporating lysine and histidine residues became of particular interest because of their basic side chains and their roles in enzymatic catalysis and molecular recognition. From a chemical perspective, the structure of this peptide reflects rational design principles. Lysine residues contribute positively charged side chains at physiological pH, influencing solubility and interactions with negatively charged biomolecules. Histidine introduces an imidazole side chain capable of proton exchange near neutral pH, a property that is central to many catalytic and binding processes in proteins. Glycine, lacking a side chain, provides conformational flexibility and often serves as a spacer within peptide sequences. The acetylation of the N2 position and amidation of the C-terminus are common modifications that reduce susceptibility to enzymatic degradation and more closely resemble post-translationally processed peptides found in nature. The application of N2-acetyl-L-lysylglycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysinamide has primarily been in biochemical and biophysical research. Short synthetic peptides of this type are frequently used as model systems to investigate peptide–protein interactions, metal ion coordination, and enzymatic recognition. The presence of histidine makes the peptide suitable for studies involving metal binding, as imidazole groups often participate in coordination with transition metals. Such properties have allowed researchers to use similar peptides to probe fundamental aspects of coordination chemistry in biological environments. In enzymology and molecular biology, peptides containing lysine and histidine residues have been employed to study protease specificity and peptide transport mechanisms. Terminally modified peptides such as this one can help distinguish between enzymatic preferences for free versus blocked termini. By comparing the behavior of acetylated and amidated peptides with their unmodified counterparts, researchers gain insight into how enzymes recognize substrates and how peptide stability can be modulated. Analytical chemistry has also benefited from the availability of well-defined peptides like N2-acetyl-L-lysylglycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysinamide. Such compounds serve as standards in chromatographic and mass spectrometric analyses, where precise molecular weight and sequence information are essential. Their predictable fragmentation patterns and solubility profiles make them useful for method development and validation in peptide analysis. Although this peptide is not associated with a direct therapeutic application, its role as a research tool is representative of a broader class of synthetic peptides that have advanced understanding in chemistry and biology. By enabling controlled variation of sequence and functional groups, compounds like N2-acetyl-L-lysylglycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysinamide have supported systematic studies of structure–function relationships at the molecular level. In summary, N2-acetyl-L-lysylglycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysinamide is a product of modern peptide chemistry whose discovery was enabled by advances in synthetic methodology. Its applications have centered on fundamental research, where it serves as a stable and informative model for studying peptide behavior, molecular interactions, and analytical techniques. Through such uses, it illustrates the enduring value of carefully designed synthetic peptides in scientific investigation. References 2025. Liposomal composition for topical administration. WO Patent. URL: WO-2025215143-A1 2025. Methods of preparing induced pluripotent stem cells from mesenchymal stem cells and methods of using the same. WO Patent. URL: WO-2025217050-A1 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for N2-Acetyl-L-lysylglycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysinamide |