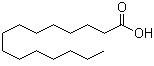
n-Pentadecanoic acid is a straight-chain saturated fatty acid consisting of fifteen carbon atoms, terminating in a carboxylic acid functional group. It belongs to the homologous series of normal, or unbranched, fatty acids that occur widely in nature. The compound is sometimes referred to as pentadecylic acid and is typically found as a minor constituent of complex lipid mixtures rather than as a dominant fatty acid. Its scientific significance is closely tied to studies of lipid composition, metabolism, and the biological origin of fatty acids.
The recognition of n-pentadecanoic acid emerged from early investigations into natural fats and oils in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. As analytical techniques for separating and characterizing fatty acids improved, chemists began to identify individual saturated and unsaturated components within animal fats, dairy products, and plant oils. Odd-chain fatty acids such as n-pentadecanoic acid attracted particular attention because most naturally occurring fatty acids contain an even number of carbon atoms, reflecting their biosynthesis from two-carbon building blocks. The presence of odd-chain fatty acids provided insight into alternative biosynthetic pathways and microbial contributions to lipid profiles.
Chemically, n-pentadecanoic acid shares the general properties of long-chain aliphatic carboxylic acids. It is a solid at room temperature, exhibits low solubility in water, and is readily soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. Its melting and boiling behavior follow predictable trends within the fatty acid series, increasing with chain length. These well-defined physical properties made n-pentadecanoic acid useful as a reference compound in studies correlating structure with thermodynamic behavior among saturated fatty acids.
The occurrence of n-pentadecanoic acid in nature is most commonly associated with ruminant fats and dairy products. It is synthesized by microorganisms in the rumen and incorporated into milk fat and adipose tissue. Because humans do not efficiently synthesize odd-chain fatty acids endogenously, the presence of n-pentadecanoic acid in human tissues and blood has been used as a biomarker of dietary intake of dairy fat. This application has been widely adopted in nutritional and epidemiological research, where objective indicators of food consumption are valuable for assessing diet-disease relationships.
Beyond its role as a dietary marker, n-pentadecanoic acid has contributed to fundamental research in lipid metabolism. Studies of its absorption, transport, and oxidation have helped clarify how odd-chain fatty acids are handled differently from even-chain analogues. In metabolic pathways, the terminal breakdown of odd-chain fatty acids yields propionyl-CoA in addition to acetyl-CoA, linking their metabolism to gluconeogenic processes. Investigations using n-pentadecanoic acid have therefore informed broader understanding of fatty acid catabolism and intermediary metabolism.
In applied chemistry, n-pentadecanoic acid has been used as a standard or internal reference in analytical methods such as gas chromatography of fatty acid methyl esters. Its defined structure and relative rarity in many samples make it suitable for calibration and quality control. It has also served as a model compound in studies of surfactant behavior, monolayer formation, and crystallization of fatty acids, where systematic variation of chain length is essential for interpreting structure–property relationships.
Although n-pentadecanoic acid does not have extensive direct industrial applications compared with more abundant fatty acids, its importance in research contexts is well established. It provides a window into microbial lipid biosynthesis, dietary assessment, and the nuanced behavior of fatty acids differing by a single carbon atom. Through these roles, n-pentadecanoic acid has contributed to both chemical knowledge and the biological sciences, illustrating how even minor natural components can have substantial scientific value.
References
2025. Understanding and improving vaccine efficacy in older adults. Nature Aging.
DOI: 10.1038/s43587-025-00939-6
2025. Impact of a Microbial and Physical Predigestion of Food Waste on the Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens (Linnaeus, 1758) Larvae Growth and Nutritional Composition. Waste and Biomass Valorization.
DOI: 10.1007/s12649-025-03246-8
|












 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details