Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Xinghua Mingwei Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (523) 8374-8465 8374-8464 | |||
 |
1344539341@qq.com tmm@msbiochem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Jintan Hunter Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (519) 8280-8688 8218-0068 | |||
 |
admin@hunterchem.com.cn | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2008 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Changzhou Share Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (519) 8261-9998 | |||
 |
wu@sharechem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Changzhou Chenqiang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (519) 8890-2455 (510) 6689-6080 +86 18015336699 | |||
 |
info@cq-chem.com sales@wxichem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1996 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Hubei Marvel-bio Medicine Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (027) 8773-8507 | |||
 |
maoerwo123@163.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: kangbao813 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2016 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Jiangsu Agrochem Laboratory | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (519) 8510-9160 | |||
 |
sales@agrochemlab.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1998 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical pesticide >> Herbicide |
|---|---|
| Name | Pyrithiobac-sodium |
| Synonyms | 2-Chloro-6-{(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)thio}benzoic acid sodium salt; Sodium 2-chloro-6-((4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)thio)benzoate; Pyrithiobac sodium salt; DPX-PE350; KIH 2031; Staple |
| Molecular Structure | 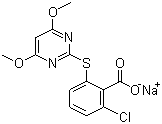 |
| Molecular Formula | C13H10ClN2NaO4S |
| Molecular Weight | 348.74 |
| CAS Registry Number | 123343-16-8 |
| EC Number | 602-931-3 |
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=NC(=N1)SC2=C(C(=CC=C2)Cl)C(=O)[O-])OC.[Na+] |
| Melting point | 233-234 ºC |
|---|---|
| Decomposition | 234 ºC |
| Water solubility | 705 g/L (pH7) |
| Hazard Symbols |


 GHS07;GHS08;GHS09 Warning Details
GHS07;GHS08;GHS09 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H319-H351-H373-H400-H410-H413 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P203-P260-P264+P265-P273-P280-P305+P351+P338-P318-P319-P337+P317-P391-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Pyrithiobac-sodium is a water-soluble herbicide belonging to the class of heterocyclic sulfonylurea compounds. It is used primarily for the control of broadleaf weeds in various agricultural and turfgrass settings. Chemically, pyrithiobac-sodium contains a pyrimidinyl-thiobenzoate core linked to a sulfonylurea functional group, with the sodium cation balancing the acidic moiety. The molecular structure allows the compound to act selectively on target plant species while maintaining low toxicity to most non-target plants and animals. The development of pyrithiobac-sodium is part of the broader research into sulfonylurea herbicides, which emerged in the 1970s as potent and selective weed control agents. Sulfonylureas inhibit the enzyme acetolactate synthase (ALS), also known as acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS), which is essential for the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids such as valine, leucine, and isoleucine in plants. By interfering with ALS activity, pyrithiobac-sodium disrupts protein synthesis in susceptible weeds, ultimately leading to growth inhibition and plant death. The selectivity of the herbicide arises from differences in enzyme sensitivity between weed species and cultivated crops. Pyrithiobac-sodium is synthesized through multi-step organic reactions that construct the pyrimidinyl-thiobenzoate core and introduce the sulfonylurea group. The sodium salt form is produced by neutralization of the acidic sulfonylurea moiety with sodium hydroxide or another suitable base. The resulting compound is water-soluble, facilitating formulation as a liquid concentrate or water-dispersible granule for field application. The solubility and stability of pyrithiobac-sodium enable precise dosage and uniform distribution when applied to soil or foliage. The herbicide is typically applied as a pre-emergent or post-emergent treatment. In pre-emergent use, pyrithiobac-sodium is incorporated into the soil, where it is absorbed by germinating seedlings through roots and shoots. Post-emergent application allows the compound to enter the foliage of young weeds, where it translocates throughout the plant and inhibits ALS. Its effectiveness at low application rates is a defining feature of sulfonylurea herbicides, minimizing environmental load while maintaining weed control efficiency. Chemically, pyrithiobac-sodium exhibits high stability under normal environmental conditions but can degrade under prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light or extreme pH. Soil adsorption characteristics influence its mobility and persistence, with sandy soils allowing greater leaching potential compared to clay-rich soils. Environmental studies have shown that the compound generally exhibits low toxicity to mammals, birds, and aquatic species at typical use concentrations, although care must be taken to avoid runoff into sensitive habitats. In agriculture, pyrithiobac-sodium is valued for its ability to control a wide spectrum of annual and perennial broadleaf weeds without harming many grass species. This selectivity allows its use in crops such as soybeans and turfgrass management, where selective weed control is critical for yield and aesthetic quality. The compound’s water solubility and ease of formulation make it suitable for various application techniques, including foliar sprays, soil incorporation, and irrigation systems. Resistance management is an important consideration in the use of pyrithiobac-sodium. Repeated use of ALS-inhibiting herbicides can select for weed populations with mutations in the ALS gene, reducing the efficacy of the compound. To mitigate resistance development, integrated weed management practices, including crop rotation, mechanical control, and alternating herbicide modes of action, are recommended. Overall, pyrithiobac-sodium is a selective, potent herbicide with a well-defined mode of action targeting ALS in susceptible weeds. Its chemical stability, water solubility, and low application rates make it a valuable tool for modern agricultural and turf management practices. By combining efficacy, selectivity, and manageable environmental impact, pyrithiobac-sodium continues to be an important component of integrated weed control strategies. References 2021. Heterosis Breeding and Hybrid Seed Production in Cotton. Hybrid Seed Production for Boosting Crop Yields. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-96-0506-4_9 2019. Chemical synthesis, crystal structure, versatile evaluation of their biological activities and molecular simulations of novel pyrithiobac derivatives. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 169. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.02.002 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Pyrithiobac-sodium |