Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Futoh Chemicals Co., Ltd. | Japan | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+81 (52) 521-8171 | |||
 |
tokoro@futoh.co.jp | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Extrasynthese Chemical S.A.S. | France | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+33 (47) 898-2034 | |||
 |
info@extrasynthese.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Win-Win Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (577) 6449-8589 +86 15325081899 | |||
 |
sales@win-winchemical.com winwinchemical@gmail.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Jingjiang Connect Chemical Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (523) 8050-1690 +86 15252623102 | |||
 |
andy@katchemical.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1998 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Classification | Flavors and spices >> Synthetic spice >> Halogen-containing, sulfur-containing, nitrogen-containing compounds >> Nitrogen-containing compound fragrance |
|---|---|
| Name | Methyl anthranilate |
| Synonyms | Methyl 2-aminobenzoate |
| Molecular Structure | 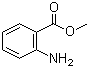 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H9NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 151.16 |
| CAS Registry Number | 134-20-3 |
| EC Number | 205-132-4 |
| FEMA | 2682 |
| SMILES | COC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1N |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 1.168 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 24 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 256.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 256 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 104.4 ºC (Calc.)*, 123 ºC (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.566 (Calc.)*, 1.582 (Expl.) |
| Water solubility | slightly soluble |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H319 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P264+P265-P280-P305+P351+P338-P337+P317 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Methyl anthranilate is an aromatic ester formed from anthranilic acid and methanol, characterized by a benzene ring bearing adjacent amino and ester functional groups. It is widely recognized for its strong, sweet, grape-like odor and has been studied extensively in the context of natural product chemistry, flavor science, and industrial applications. The history of methyl anthranilate is closely tied to the broader investigation of aromatic esters and amino-substituted benzoic acid derivatives. The discovery of methyl anthranilate can be traced to nineteenth-century research on anthranilic acid, which itself was identified as an important intermediate in the chemistry of indigo dyes and other aromatic compounds. As esterification reactions became better understood, chemists prepared methyl anthranilate as part of systematic studies on anthranilic acid derivatives. Early characterization focused on its physical properties, distinctive odor, and chemical reactivity, which set it apart from many other simple aromatic esters. Chemically, methyl anthranilate exhibits properties that reflect the influence of both its ester group and its ortho-amino substituent. The proximity of the amino group to the ester functionality affects intramolecular interactions and contributes to its relatively high stability among aromatic esters. These features made methyl anthranilate a useful model compound in studies of structure–property relationships within substituted benzoates. Its synthesis, typically achieved through acid-catalyzed esterification of anthranilic acid or through related transesterification routes, became well established in laboratory and industrial settings. One of the most significant applications of methyl anthranilate has been in the flavor and fragrance industries. It occurs naturally in a variety of fruits and flowers, including grapes, strawberries, and jasmine, and it is a key contributor to characteristic aroma profiles. Because of this natural association, methyl anthranilate has been widely used as a flavoring agent to impart grape-like notes in foods and beverages, as well as a fragrance component in perfumes, soaps, and personal care products. Its sensory properties and relative chemical stability have supported its long-standing commercial use. Beyond flavor and fragrance applications, methyl anthranilate has played an important role in agricultural and environmental contexts. It has been investigated and employed as a bird repellent, exploiting its odor to deter birds from crops, airfields, and other sensitive areas. This application emerged from behavioral studies demonstrating aversive responses in certain bird species. The compound’s effectiveness, combined with its relatively low persistence in the environment, contributed to its adoption in non-lethal wildlife management strategies. Methyl anthranilate has also been relevant in organic synthesis and chemical research. The compound serves as a precursor or intermediate in the preparation of more complex molecules, including heterocyclic compounds derived from anthranilic acid frameworks. Its reactivity has been explored in transformations involving the amino group, such as acylation and cyclization reactions, making it useful in teaching laboratories and synthetic methodology development. In biological and toxicological studies, methyl anthranilate has been examined to assess safety and exposure, particularly because of its widespread use in consumer products. These investigations have helped define acceptable usage levels and informed regulatory evaluations in different jurisdictions. Such studies reinforced its suitability for use in food and fragrance applications when handled according to established guidelines. Overall, methyl anthranilate exemplifies how a relatively simple organic molecule can achieve broad scientific and practical significance. From its origins in fundamental aromatic chemistry to its diverse applications in flavoring, fragrance, agriculture, and synthesis, the compound illustrates the intersection of chemical discovery and applied science. Its continued relevance reflects both its distinctive sensory properties and its versatility as a chemically well-understood aromatic ester. References 2025. Assessing the efficacy of nanofabricated plant-based antifungal formulation against the growth and zearalenone toxin production by Fusarium graminearum. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology. DOI: 10.1007/s42770-025-01744-4 2025. Engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the synthesis of aromatic compounds. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-025-13520-3 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Methyl anthranilate |