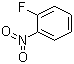
1‑Fluoro‑2‑nitrobenzene is an aromatic compound characterized by the presence of a fluorine atom at the first position and a nitro group at the second position of a benzene ring. Its molecular formula is C6H4FNO2. The ortho relationship between the fluorine and nitro substituents imparts unique chemical and physical properties, including reactivity patterns that differ from meta- and para-substituted analogues. It is a pale yellow liquid under standard conditions with moderate solubility in organic solvents and limited solubility in water, reflecting the combined polar effects of the nitro and fluoro substituents.
The discovery and study of 1‑fluoro‑2‑nitrobenzene are linked to research on halonitrobenzenes, which have long been important intermediates in organic synthesis, dye chemistry, and pharmaceutical development. The compound’s ortho-substitution pattern affects both electronic and steric properties, influencing reactions such as nucleophilic aromatic substitution and reduction. The electron-withdrawing effect of the nitro group activates the aromatic ring toward nucleophilic attack at positions ortho and para to itself, while the fluorine atom stabilizes the ring through inductive effects and participates in hydrogen bonding in solid-state structures. These characteristics make 1‑fluoro‑2‑nitrobenzene a versatile building block in synthetic chemistry.
1‑Fluoro‑2‑nitrobenzene is typically synthesized by electrophilic nitration of fluorobenzene under controlled conditions. The reaction involves treatment of fluorobenzene with a nitrating mixture, often concentrated nitric and sulfuric acids, at low temperatures to favor the ortho product. Temperature control, stoichiometry, and reaction time are critical to minimize formation of meta- and para-isomers and to prevent overnitration. The resulting 1‑fluoro‑2‑nitrobenzene can be purified by fractional distillation or recrystallization, depending on its physical form and impurities present.
Chemically, 1‑fluoro‑2‑nitrobenzene undergoes a variety of reactions typical of halonitroarenes. The fluorine atom, while relatively inert, can act as a leaving group in nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions, particularly when the nitro group is positioned ortho or para to it. This enables the introduction of nucleophiles such as amines, alkoxides, or thiolates, providing functionalized aromatic derivatives. The nitro group itself can be selectively reduced to an amino group, forming 2‑fluoroaniline, or converted into other functionalities such as hydroxyl, amide, or azide groups, depending on the reaction conditions.
1‑Fluoro‑2‑nitrobenzene is commonly used as a precursor in pharmaceutical and agrochemical synthesis. Its ortho-substitution pattern allows selective derivatization, enabling the construction of biologically active molecules, including heterocyclic compounds, inhibitors, and intermediates for drug candidates. In dye and material chemistry, it is employed as a starting material for azo compounds, nitroaromatic polymers, and other functionalized materials, leveraging the reactivity of the nitro and fluoro substituents to modify electronic and steric properties.
From a physical and safety perspective, 1‑fluoro‑2‑nitrobenzene is volatile and should be handled with appropriate precautions. It is flammable and can irritate the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. Proper protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and fume hoods, is recommended when handling this compound. It is stable under normal storage conditions but should be kept away from strong reducing agents or bases, which can react with the nitro group or promote elimination reactions.
Overall, 1‑fluoro‑2‑nitrobenzene is a chemically versatile aromatic halonitro compound with applications in organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. Its ortho-substitution of a fluorine atom and nitro group provides a combination of reactivity and selectivity that allows chemists to construct functionalized aromatic compounds efficiently. The balance of electronic effects, steric properties, and chemical stability makes 1‑fluoro‑2‑nitrobenzene an important building block for laboratory and industrial chemical processes.
References
2025. Synthesis of New 1,3a,6,6a-Tetraazapentalene Derivatives under Cadogan Reaction Conditions. Russian Journal of Organic Chemistry.
DOI: 10.1134/s1070428025601761
|




















 GHS06;GHS07;GHS08 Danger Details
GHS06;GHS07;GHS08 Danger Details