Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Hydrocarbon compounds and their derivatives >> Hydrocarbon halide |
|---|---|
| Name | 1-Chlorooctadecane |
| Synonyms | Stearyl Chloride; Octadecyl chloride |
| Molecular Structure | 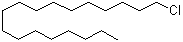 |
| Molecular Formula | C18H37Cl |
| Molecular Weight | 288.94 |
| CAS Registry Number | 3386-33-2 |
| EC Number | 222-207-7 |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCl |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 0.849 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 20 - 23 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 347.8±5.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 402.4 - 403.9 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 151.9±3.4 ºC (Calc.)*, 20 ºC (Expl.) |
| Solubility | water: 0.03 g/L (20 ºC) (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.448 (Calc.)*, 1.451 (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H317-H319-H335-H413 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P272-P273-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P333+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1-Chlorooctadecane is a straight-chain alkyl halide consisting of an 18-carbon saturated hydrocarbon chain with a chlorine atom bonded to the terminal carbon. Its molecular formula is C18H37Cl. The compound is a colorless to pale yellow liquid under standard conditions, with low solubility in water and good solubility in nonpolar organic solvents such as hexane, benzene, and chloroform. Its long hydrophobic chain and terminal chlorine atom confer both lipophilicity and moderate chemical reactivity. The discovery and use of 1-chlorooctadecane are part of the broader study of long-chain alkyl halides, which have been employed historically in organic synthesis and materials science. Terminal chlorides serve as reactive sites for nucleophilic substitution reactions, making 1-chlorooctadecane a useful intermediate in the preparation of surfactants, quaternary ammonium salts, and functionalized long-chain derivatives. The stability of the saturated hydrocarbon chain combined with the reactive chlorine atom allows selective chemical transformations without affecting the hydrocarbon backbone. Synthesis of 1-chlorooctadecane is typically carried out via substitution reactions of 1-octadecanol or corresponding alkanes. A common approach involves treatment of 1-octadecanol with thionyl chloride, phosphorus pentachloride, or other chlorinating agents under controlled conditions to replace the hydroxyl group with chlorine. Reaction parameters such as temperature, solvent, and reagent stoichiometry are carefully optimized to avoid side reactions like elimination or over-chlorination. The final product is purified by distillation or recrystallization to yield pure 1-chlorooctadecane. Chemically, 1-chlorooctadecane exhibits the reactivity characteristic of primary alkyl chlorides. The terminal chlorine atom can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions to produce alcohols, amines, or other functionalized derivatives. It can also participate in elimination reactions under basic conditions to generate alkenes. The long alkyl chain imparts hydrophobicity and affects the compound’s melting and boiling points, as well as its solubility in various solvents. These properties make 1-chlorooctadecane a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis and materials modification. In practical applications, 1-chlorooctadecane is used in the synthesis of surfactants, lubricants, phase transfer catalysts, and cationic or nonionic derivatives for industrial and laboratory purposes. It is also employed in organic chemistry for the preparation of long-chain functional molecules, including alkylated heterocycles and polymers. The compound’s hydrophobic tail and reactive terminal chlorine allow it to serve as a building block for amphiphilic molecules and self-assembling monolayers in materials research. From a physical and safety perspective, 1-chlorooctadecane is generally stable under ambient conditions but should be protected from strong bases or nucleophiles that may induce unwanted reactions. It is flammable and should be handled with appropriate precautions, including the use of gloves, goggles, and ventilation to prevent skin contact, inhalation, or accidental ignition. Overall, 1-chlorooctadecane is a long-chain alkyl halide with significant chemical versatility due to its terminal chlorine atom and hydrophobic octadecyl chain. Its use as a synthetic intermediate in organic chemistry, surfactant production, and materials modification highlights the utility of long-chain chlorides in chemical research and industrial applications. The combination of chemical reactivity, stability, and lipophilicity makes it a valuable compound for both laboratory and commercial synthesis. References 2025. Selecting effective plant species for the phytoremediation of persistent organic pollutants and multielement contaminated fibrous sediments. Environmental Sciences Europe. DOI: 10.1186/s12302-025-01168-9 2025. Hydrophobic modification of activated carbon using stearyl chloride for enhanced VOCs adsorption under high-humidity conditions. Journal of Materials Science. DOI: 10.1007/s10853-025-11059-2 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 1-Chlorooctadecane |