Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Eastar Chemical Corporation | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 800-898-2436 | |||
 |
info@eastarchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1989 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2014 | ||||
| Shanghai Hongbang Medical Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 2428-0809 +86 13671516988 | |||
 |
kimberly-hongbangpharma@hotmail.com 1377976036@qq.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2014 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Cangzhou Enke Pharma-tech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (317) 510-5699 510-6597 +86 15533709196 | |||
 |
sale@enkepharma.com enkepharma@126.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: ymzhao | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2011 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2016 | ||||
| Auben Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 19121901603 | |||
 |
sales@aubenchem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2023 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Analytical chemistry >> Standard >> Pharmacopoeia standards and magazine standards |
|---|---|
| Name | D-(+)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid |
| Synonyms | DL-Camphor sulfonic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 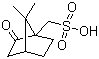 |
| Molecular Formula | C10H16O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 232.30 |
| CAS Registry Number | 5872-08-2 |
| EC Number | 227-527-0 |
| SMILES | CC1(C2CCC1(C(=O)C2)CS(=O)(=O)O)C |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 200 ºC (Decomposes) (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.54 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS05 Danger Details
GHS05 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H314 Details | ||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P264-P280-P301+P330+P331-P302+P361+P354-P304+P340-P305+P354+P338-P316-P321-P363-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 3261 | ||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||
|
D-(+)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid is a naturally derived, chiral organosulfur compound obtained from camphor. Its molecular formula is C10H16O4S. Structurally, it consists of a bicyclic camphor skeleton with a sulfonic acid (-SO3H) group at the 10-position, imparting strong acidity and hydrophilicity to the molecule. It is typically encountered as a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents, while being insoluble in nonpolar solvents. The chiral bicyclic framework imparts optical activity, and the D-(+) enantiomer is widely used in stereoselective applications. The discovery and application of D-(+)-10-camphorsulfonic acid are closely associated with asymmetric synthesis and enantioselective catalysis. The compound has been recognized for its ability to induce chirality in chemical reactions, particularly in the resolution of racemic amines and alcohols, and in promoting enantioselective transformations when used as a chiral counterion or acid catalyst. The rigid, sterically defined camphor skeleton allows selective interactions with substrates, facilitating asymmetric induction in reactions such as alkylations, Michael additions, and cyclizations. Synthesis of D-(+)-10-camphorsulfonic acid generally involves the sulfonation of naturally occurring D-(+)-camphor using concentrated sulfuric acid or fuming sulfuric acid under controlled temperature. The reaction is conducted to introduce the sulfonic acid group selectively at the 10-position of the camphor ring. The resulting product is purified by crystallization from water or ethanol, yielding the D-(+) enantiomer in high optical purity. This method preserves the chiral integrity of the camphor backbone and produces a stable, crystalline sulfonic acid. Chemically, D-(+)-10-camphorsulfonic acid is a strong acid, capable of protonating basic functional groups and forming salts with amines, metals, or other cationic species. The chiral environment provided by the camphor skeleton allows the formation of diastereomeric salts when paired with racemic compounds, which is exploited in resolution procedures to separate enantiomers. Its sulfonic acid functionality is also reactive in forming esters or sulfonamides for further chemical modification. In practical applications, D-(+)-10-camphorsulfonic acid is extensively used as a chiral resolving agent in the pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries. It is employed to resolve racemic amines and alcohols into their enantiomerically pure forms, which is critical for drug synthesis, where stereochemistry directly impacts biological activity and safety. Additionally, it serves as a chiral acid catalyst in asymmetric synthesis, facilitating enantioselective reactions with high efficiency and selectivity. Beyond chemical synthesis, its strong acidity and water solubility allow its use in organic and inorganic salt formation, phase-transfer catalysis, and ionic liquid preparation. Physically, the compound is thermally stable and can be stored as a crystalline solid in a dry, cool environment. It is hygroscopic and should be protected from moisture to maintain its solid-state purity. Standard laboratory safety precautions should be observed, including gloves and eye protection, as strong acids can cause irritation or chemical burns. Overall, D-(+)-10-camphorsulfonic acid is a chiral, bicyclic sulfonic acid with significant utility in asymmetric synthesis, enantiomeric resolution, and chiral catalysis. Its combination of strong acidity, stereochemically defined framework, and solubility in polar solvents makes it an indispensable tool in modern organic chemistry and pharmaceutical development, particularly for the production of enantiomerically pure compounds and enantioselective reactions. References 2025. (�)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid catalyzed effective synthesis of a,�-unsaturated �-aminoketones from enaminone. Monatshefte f�r Chemie - Chemical Monthly. DOI: 10.1007/s00706-025-03329-1 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for D-(+)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid |