Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Yujiao Bio-chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 17060324263 | |||
 |
ficherchem@gmail.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2016 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2023 | ||||
| RC Chemicals Lab Inc | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (401) 232-4508 | |||
 |
info@rcchemicallabs.net | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | API >> Anesthetic agents >> General anesthetics |
|---|---|
| Name | Ketamine |
| Synonyms | 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexan-1-one |
| Molecular Structure | 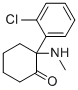 |
| Molecular Formula | C13H16ClNO |
| Molecular Weight | 237.73 |
| CAS Registry Number | 6740-88-1 |
| EC Number | 229-804-1 |
| SMILES | CNC1(CCCCC1=O)C2=CC=CC=C2Cl |
| Solubility | 3870 mg/L (25 ºC water) |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3, Calc.* |
| Index of Refraction | 1.562, Calc.* |
| Melting point | 109.56 ºC |
| Boiling Point | 339.74 ºC, 363.8±42.0 ºC (760 mmHg), Calc.* |
| Flash Point | 173.8±27.9 ºC, Calc.* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302+H332-H302-H332 Details | ||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P270-P271-P301+P317-P304+P340-P317-P330-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Controlled Substance | DEA Drug Code Number: 7285 Details | ||||||||||||||||
| CSA Schedule: III | |||||||||||||||||
| Narcotics? No | |||||||||||||||||
|
Ketamine is a synthetic arylcyclohexylamine compound primarily used as a dissociative anesthetic in human and veterinary medicine. Its molecular formula is C13H16ClNO. Structurally, ketamine consists of a cyclohexanone ring substituted with a chlorophenyl group at the 2-position and an amino group at the 1-position, forming (RS)-2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexanone. It appears as a white crystalline solid or as a clear, colorless solution in its hydrochloride salt form and is soluble in water and polar organic solvents such as ethanol and propylene glycol. Ketamine was first synthesized in 1962 by Calvin Stevens at Parke-Davis. It was developed as a safer alternative to phencyclidine (PCP), with reduced psychotomimetic side effects and a more favorable safety profile. The drug produces a dissociative anesthesia, characterized by analgesia, amnesia, and catalepsy, without necessarily inducing complete loss of consciousness. Its mechanism of action involves noncompetitive antagonism of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, which inhibits excitatory neurotransmission in the central nervous system. Ketamine also interacts with opioid receptors, monoaminergic systems, and voltage-gated calcium channels, contributing to its analgesic and antidepressant effects. Synthesis of ketamine typically involves the condensation of 2-chlorobenzonitrile with cyclopentyl magnesium bromide to generate a substituted cyclohexanone intermediate, followed by reaction with methylamine to introduce the amino group at the 2-position. The resulting racemic mixture can be converted into ketamine hydrochloride for pharmaceutical use. Enantioselective synthesis can produce (S)-ketamine or (R)-ketamine, which differ in potency and pharmacological profile. Purification is performed using recrystallization or chromatographic techniques to achieve high chemical and optical purity. Chemically, ketamine is a chiral amine with a ketone functional group and a chlorophenyl substituent, which confers lipophilicity and allows penetration of the blood-brain barrier. The molecule is stable under standard laboratory conditions but can undergo oxidation at the ketone to form norketamine, an active metabolite. Ketamine’s nitrogen atom enables salt formation, typically as the hydrochloride, to increase water solubility for injectable formulations. In practical applications, ketamine is widely used as an anesthetic for induction and maintenance of anesthesia in humans and animals. Its rapid onset and short duration make it suitable for outpatient procedures and field anesthesia. Ketamine is also used for analgesia in acute pain management and procedural sedation. In recent years, (S)-ketamine has been approved as a nasal spray for treatment-resistant depression, reflecting its NMDA receptor-mediated antidepressant properties. Additionally, ketamine is used in research to study synaptic plasticity, neuroprotection, and NMDA receptor pharmacology. Physically, ketamine hydrochloride is stable at room temperature when stored in a dry, protected environment. Handling precautions include the use of gloves and eye protection, as ketamine is psychoactive and can cause dissociation or other central nervous system effects upon accidental exposure. Its use is strictly regulated in most countries due to potential for abuse. Overall, ketamine is a versatile dissociative anesthetic and pharmacologically active compound. Its NMDA receptor antagonism, combined with analgesic and antidepressant effects, makes it an essential tool in medicine and research. Ketamine’s unique combination of rapid onset, multiple administration routes, and safety profile continues to support its widespread clinical and scientific applications. References 2025. Efficacy and safety of esketamine for smoking cessation among patients diagnosed with lung cancer and major depression disorder: A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Journal of Affective Disorders. DOI: 10.1016/j.jad.2025.04.077 2025. Utilizing depression symptom-based phenotypes to explore ketamine treatment response in major depression: The Bio-K multicenter trial. Journal of Affective Disorders. DOI: 10.1016/j.jad.2025.119414 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Ketamine |