Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hangzhou Verychem Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8816-2785 +86 13606544505 | |||
 |
lucy@verychem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2004 | ||||
| chemBlink massive supplier since 2021 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Shanghai Fuxin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 3130-0828 +86 18645121291 | |||
 |
contact@fuxinpharm.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2016 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2018 | ||||
| Shanghai Baoyu International Trade Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 5271-3053 | |||
 |
jby@chinabychem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| P and M Invest Ltd. | Russia | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+7 (495) 135-6494 | |||
 |
sales@fluorine1.ru | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Sinbond Industrial Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (531) 8703-8285 +86 13583181986 +44 (208) 242-5518 | |||
 |
cici1124@gmail.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2014 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Fatty acid |
|---|---|
| Name | Chlorodifluoroacetic acid |
| Synonyms | 2-Chloro-2,2-difluoroacetic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 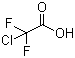 |
| Molecular Formula | C2HClF2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 130.48 |
| CAS Registry Number | 76-04-0 |
| EC Number | 200-928-8 |
| SMILES | C(=O)(C(F)(F)Cl)O |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 1.54 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 20 - 23 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 119.2±35.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 122 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 25.9±25.9 ºC (Calc.)*, 23 ºC (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.376 (Calc.)*, 1.355 (Expl.) |
| Water solubility | soluble |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS05 Danger Details
GHS05 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H314-H318 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P264-P264+P265-P280-P301+P330+P331-P302+P361+P354-P304+P340-P305+P354+P338-P316-P317-P321-P363-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 3261 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Chlorodifluoroacetic acid is a halogenated carboxylic acid characterized by the presence of one chlorine atom and two fluorine atoms attached to the acetic acid backbone. As a small, strongly electron-withdrawing molecule, it occupies an important position in fluorine chemistry and has been used primarily as a building block and reagent in organic synthesis. Its properties reflect the combined effects of fluorine and chlorine substitution, which significantly alter acidity, reactivity, and physicochemical behavior compared with unsubstituted acetic acid. The identification and preparation of chlorodifluoroacetic acid arose from broader efforts in the mid twentieth century to explore halogenated organic acids. As fluorine chemistry advanced, chemists recognized that fluorinated carboxylic acids exhibited enhanced acidity and distinctive reactivity patterns. Chlorodifluoroacetic acid was developed as part of systematic studies on partially fluorinated acetic acids, which bridged the gap between simple haloacetic acids and fully fluorinated analogues. These investigations aimed to understand how incremental halogen substitution influenced molecular properties and synthetic utility. From a chemical standpoint, chlorodifluoroacetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid due to the strong inductive electron-withdrawing effects of the chlorine and fluorine atoms. These substituents stabilize the conjugate base by dispersing negative charge, resulting in increased acid strength. The molecule is typically a colorless liquid or crystalline solid, depending on temperature and purity, and is miscible with many polar organic solvents. Its reactivity is dominated by the carboxylic acid functional group, while the halogenated methyl group remains relatively inert under many reaction conditions. In organic synthesis, chlorodifluoroacetic acid has been used as a precursor for a variety of chlorodifluoromethyl-containing compounds. The chlorodifluoromethyl group is of interest because it can act as a bioisosteric replacement for other functional groups, modifying lipophilicity and metabolic stability in target molecules. Through conversion of the acid to derivatives such as acid chlorides, esters, or amides, chemists can introduce the chlorodifluoroacetyl moiety into more complex molecular frameworks. These transformations have supported research in medicinal chemistry, agrochemical development, and materials science. Another important application of chlorodifluoroacetic acid lies in its use as a reagent or intermediate in fluorination chemistry. The presence of both chlorine and fluorine atoms makes it a versatile substrate for substitution or elimination reactions under controlled conditions. In some contexts, it has been used to generate chlorodifluoromethyl radicals or related reactive species, enabling the construction of carbon–carbon and carbon–heteroatom bonds that incorporate fluorinated motifs. Such reactions are valuable for accessing compounds with tailored electronic and steric properties. Chlorodifluoroacetic acid has also played a role in mechanistic and physical organic chemistry studies. By comparing its behavior with that of mono- and trifluorinated acetic acids, researchers have gained insights into substituent effects on acidity, reaction kinetics, and solvation. These comparative studies have contributed to a deeper understanding of how halogen substitution influences fundamental chemical properties, informing the rational design of fluorinated molecules. In industrial and applied research settings, chlorodifluoroacetic acid has been handled with care due to its corrosive nature and the general reactivity of halogenated acids. Appropriate safety measures are required to manage its acidity and potential to release hydrogen halides under certain conditions. Despite these considerations, its utility as a synthetic intermediate has ensured continued interest and use in specialized chemical applications. Overall, chlorodifluoroacetic acid exemplifies the importance of halogenated small molecules in modern chemistry. Its discovery emerged from systematic exploration of fluorinated acids, and its applications have centered on its role as a versatile intermediate and reagent. By combining enhanced acidity with the distinctive properties of fluorine and chlorine substitution, chlorodifluoroacetic acid has contributed to advances in synthetic methodology, fluorine chemistry, and the development of functional organic compounds. References 2024. Recent advances in silver-mediated/catalyzed synthesis of trifluoromethoxy compounds. Science China Chemistry. DOI: 10.1007/s11426-024-2342-4 2023. Comprehensive characterization of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in wastewater by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and screening algorithms. npj Clean Water. DOI: 10.1038/s41545-023-00220-6 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Chlorodifluoroacetic acid |